Rotator Cuff Tear
What is a Rotator Cuff Tear?
A rotator cuff is a group of tendons in the shoulder joint that provides support and enables a wide range of motion. A major injury to these tendons may result in rotator cuff tears. It is one of the most common causes of shoulder pain in middle-aged and older individuals, where it is estimated that around 20% of these populations may have a tear in their rotator cuff.

Causes
A rotator cuff tear may occur with repeated use of the arm for overhead activities, while playing sports, or from a motor accident.
Symptoms
A rotator cuff tear causes severe pain, weakness of the arm and crackling sensation on moving the shoulder in certain positions. There may be stiffness, swelling, loss of movement and tenderness in the front of the shoulder.
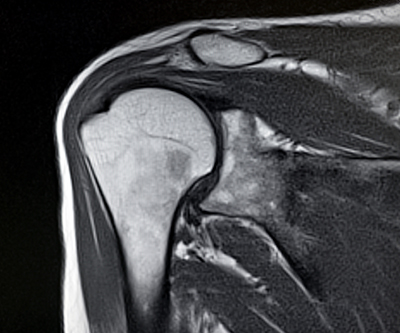
Diagnosis
Your surgeon diagnoses a rotator cuff tear based on a physical examination and X-rays. A rotator cuff tear is best viewed on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
There are a variety of tests that your provider may perform in order to determine if you have a rotator cuff tear:
- MRI Scan: A MRI scan shows the soft tissues, including the tendons, muscles, and ligaments of your shoulder. It is the best test that your provider can use to accurately diagnose a rotator cuff tear.
- X-Ray: An x-ray can be used to see if there are any fractures or injury to the bones of your shoulder.
- Physical examination: Your doctor might examine your shoulder by maneuvering to test the range of motion, joint stability, and pain that may indicate a rotator cuff tear.

Treatment Options
Conservative treatment
The conservative treatment options for rotator cuff tears are:
- Rest and activity modification: Your provider may recommend rest and to avoid certain activities that aggravate your symptoms to reduce pain and further damage.
- Shoulder Sling: If the patient has significant pain while using their shoulder, your orthopedic surgeon may recommend putting your shoulder in a sling to prevent pain and further injury.
- Pain medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs) medication may be recommended, as it can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Injection of a steroid with a local anesthetic: Can help relieve inflammation and pain
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the shoulder
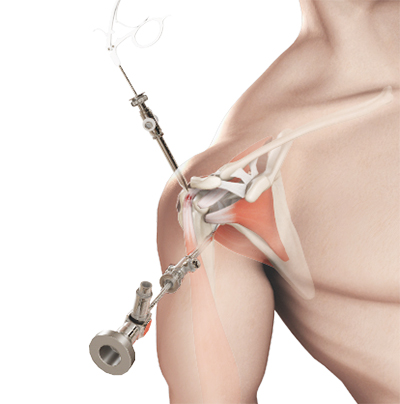
Surgical Options
Rotator cuff repair may be performed by open or arthroscopic surgery. In arthroscopy, the tear is repaired using small keyhole incisions to allow for an arthroscope, a medical instrument with a light and small camera, to access the joint and repair damage. The surgery requires the use of suture anchors, which help in attaching the tendons to the shoulder bone. Following the surgery, you may participate in physical therapy, where you can work to regain motion and strength of the joint.
