Hip Arthroscopy
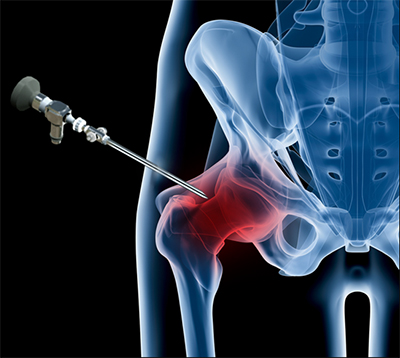
What is Hip Arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, is a procedure in which an arthroscope is inserted into a joint to check for any damage and repair it simultaneously. An arthroscope is a small, fiber-optic instrument consisting of a lens, light source, and video camera.
The advantages of hip arthroscopy over the traditional open hip surgery include:
- Smaller incisions
- Minimal trauma to surrounding ligaments, muscles, and tissues
- Less pain
- Faster recovery
- Lower infection rate
- Less scarring
- Early mobilization
- Shorter hospital stay
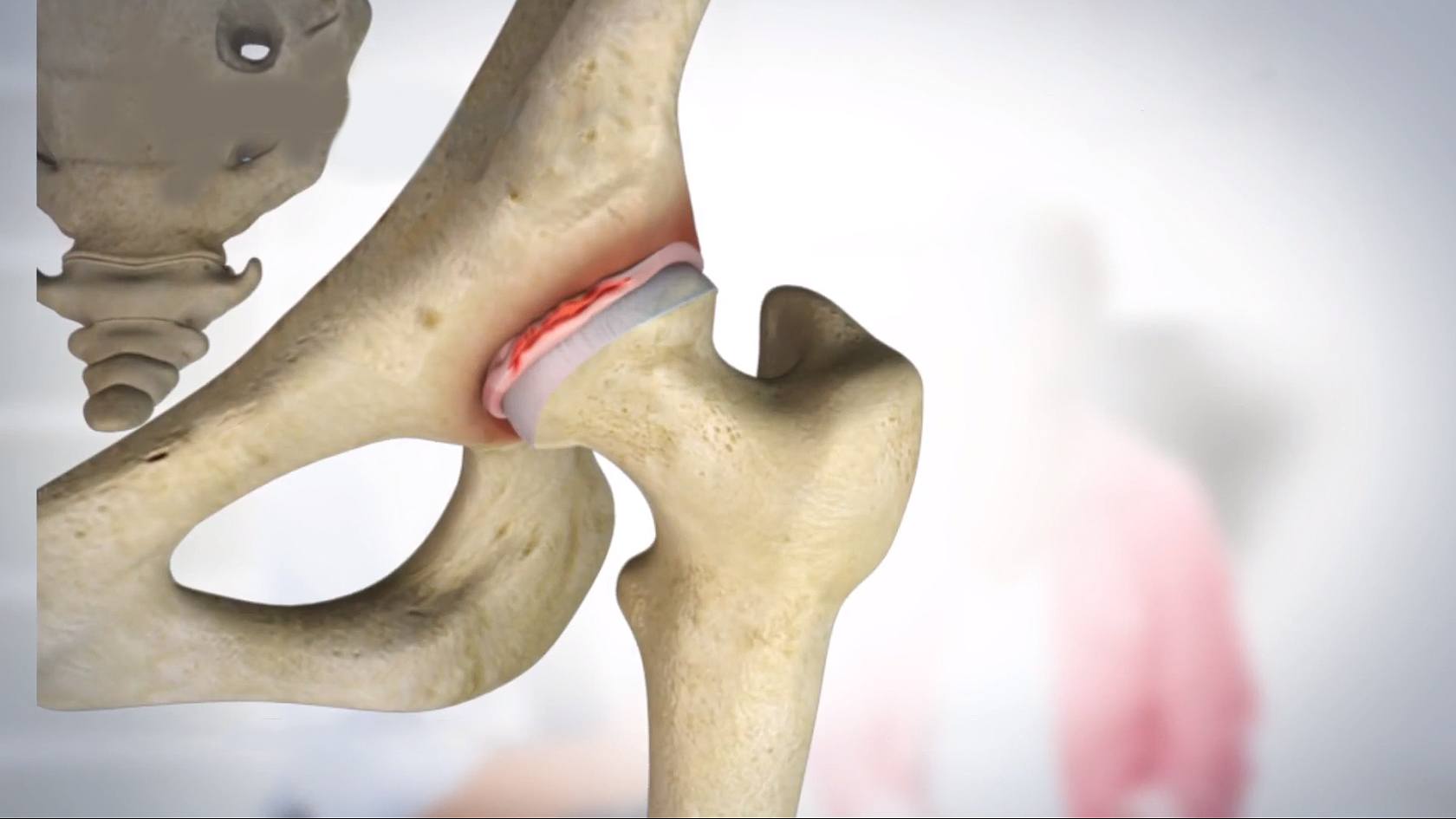
Indications
Hip arthroscopy can be used to treat a variety of conditions in the hip:
- Removal of torn cartilage (labral tears or cartilage defects) or bone chips (loose bodies) that cause hip pain and immobility
- Arthroscopic labral repair: Repair a torn labrum (fibrous cartilage ring that lines the acetabular socket)
- Arthroscopic femoroplasty & acetabuloplasty: This surgical treatment is used for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome. These procedures involve the removal of extra bone growth on the femur (ball) or acetabulum (socket).
- Arthroscopic synovectomy: Removal of part of the inflamed synovium (lining of the joint) in patients with inflammatory arthritis (partial synovectomy)
- Repair of fractures and torn ligaments, and removal of bone spurs or extra bone growths caused by arthritis or an injury.
- Diagnostic hip arthroscopy: Evaluation and diagnosis of conditions with unexplained pain, swelling, or stiffness in the hip that does not respond to conservative treatment
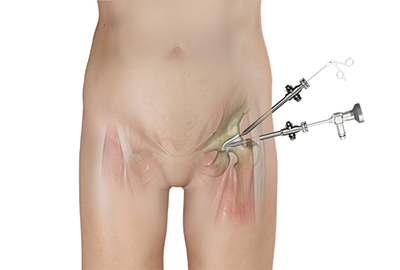
Description of Procedure
Patients undergoing hip arthroscopy will receive general anesthesia. The surgeon will start by making keyhole incisions around the hip joint. This allows them to put the arthroscope into the incisions and to look into the joint. Your orthopedic surgeon will then perform a diagnostic hip arthroscopy, meaning they examine the structures of the inside of the hip to understand the extent of the injuries. Following the diagnostic hip arthroscopy, your surgeon will repair or remove structures that are causing you pain.

Post Operative Care
Your doctor may advise you to take certain precautions to promote faster recovery and prevent further complications. These include:
- Taking pain medications as prescribed
- Use of crutches to prevent or limit bearing weight on the operated hip
- Physical therapy exercises should be performed to restore normal hip function and improve flexibility and strength
- Eating a healthy diet and avoiding smoking will help in faster healing and recovery
- Avoid activity which involves lifting heavy things or strenuous exercises for the first few weeks after surgery
