Loose Bodies
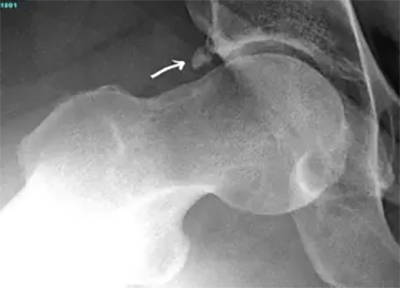
What is a Loose Body?
A loose body is a small piece of cartilage or bone that is floating within the joint. Loose bodies can cause sharp pain and may even cause a person to feel their joint is giving way. Loose bodies can at times be secondary to a previous hip surgery or reinjury.
What Causes a Loose Body to Form?
A loose body can happen gradually over time or from traumatic accidents. Overtime, if a person has arthritis, abnormal bony growths, avascular necrosis, or unhealthy bones they can develop loose bodies. Trauma from automobile accidents can directly trigger or lead to the formation of a loose body within the hip as well.

What are the Symptoms of Loose Bodies?
Some common symptoms of loose bodies are listed below:
- Catching or locking of the hip
- Dull aching in the hip after movement
- Pain while squatting
- Popping or snapping in the hip
- Feeling like the hip is going to “give out”
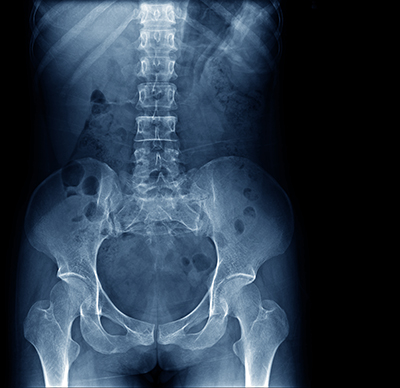
Diagnosis of Loose Bodies
Your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms and based on this a physical examination will be performed. Your doctor may also recommend the following diagnostic tests:
Physical Examination: By performing a variety of tests, a clinician can use provocative tests that can help indicate the presence or lack of presence of loose bodies. Physical examination also helps rule out other possible issues with the lower extremities and back.
X-rays: This study uses electromagnetic beams to produce images of the bones and can show if there are loose bodies in the bone surrounding the hip joint.
MRI Scan: This is an imaging study that uses a large magnetic field and radio waves to detect any damage to the soft tissues. Sometimes loose bodies can attach to and aggravate soft tissue.
Ultrasound: This study uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the tissues of the hip.

What are the Treatments for Loose Bodies?
For loose bodies, conservative treatments include:
- Applying heat and ice to the area of pain
- Activity modification
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) medications
- Physical therapy
- Therapeutic injections such as cortisone
Surgical Treatments
If a loose body is identified and the patient's symptoms are serious, a physician may recommend surgical treatment. Below are different types of surgical treatment often used when for loose bodies:
- Loose body removal with or without synovectomy
- Labral repair or reconstruction
- Femoroplasty
- Acetabuloplasty
After the procedure, a patient may likely undergo physical therapy to regain mobility, strength, and function in the hip. Depending on the procedures performed and the patient, the rehabilitation process can range from several weeks to several months.
